Nominal Interest Rate Definition Economics
1 i 1 r 1 π it requires a multi step mathematical process to derive one of these equations from the other but both.
Nominal interest rate definition economics. This interest rate will be quoted on things like loans bonds and the like. Differences between real and nominal rates. R r i or 1 r 1 r 1 e r. In finance and economics the nominal interest rate refers to the interest rate without the adjustment of inflation.
Nominal interest rate definition. If the lender is receiving 8 from a loan and inflation is 8 then the real rate of. In finance and economics the nominal interest rate or nominal rate of interest is either of two distinct things. It is basically the rate as stated as advertised and so on which does not take inflation compounding effect of interest tax or any fees in the account.
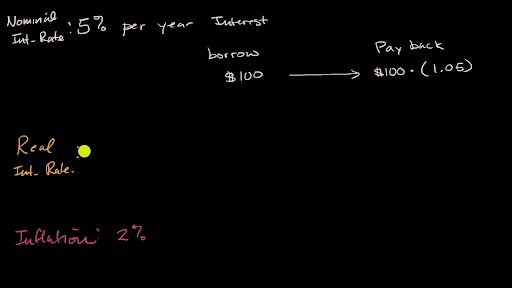
The nominal interest rate is the stated interest rate of a bond or loan which signifies the actual monetary price borrowers pay lenders to use their money. The real rate is the nominal rate minus inflation. The interest rate is the rate at which interest is paid by a borrower debtor for the use of money borrowed from a lender creditor. The rate of interest before adjustment for inflation.
Nominal rate refers to the rate before adjustment for inflation. The interest rate is one of the primary influences on economic rationale. The difference between real and nominal interest rates can be represented using the fisher equation. If one makes a loan at a high nominal interest rate this does not guarantee a real profit for example if the nominal interest rate on a loan is 7 and the inflation rate is 4 the real interest rate is only 3.
It is the rate as advertised which will not necessarily reflect the reality of how the interest rate will. Interest rates and economic rationale. For interest rates as stated without adjustment for the full effect of compounding also referred to as the nominal annual rate an interest rate is called nominal if the. If the nominal rate on a loan is 5.
The rate of interest before adjustment for inflation in contrast with the real interest rate. Nominal interest rates may be held at artificially low levels after a major recession to stimulate economic activity through low real interest rates which encourage consumers to take out loans. In finance and economics nominal interest rate or nominal rate of interest refers to two distinct things. Nominal interest rate definition.
I r π where i is the nominal interest rate r is the real interest rate and π is the rate of inflation. If the nominal interest rate is 1 and inflation is 3 the real interest rate is 2. The real rate is the nominal rate minus inflation. The nominal interest rate is the interest rate that has not yet had inflation accounted for in the overall number.
What does nominal interest rate mean. Economists manipulate this equation to read. Examples of nominal interest rate in the following topics.